Summer Expedition to the Jura, France.
27th July – 10th August 2019
Lead contact: Gary Vaughan
Phone: 07836 727131 E-Mail: gary@dorsetland.co.uk
INFO
LINKS
Jura Info
The South Wales Caving Club Expedition
To
The Franche Comte
(The Jura and the Doubs)
27th July – 10th August 2019
Franche-Comté is the name given to the vast area of woodland which lies to the north of the French Alps in Eastern France, and stretches southward along the Swiss border for 250km, from Vosges to the Jura. The region is divided into four different départements, the Haute-Saône, Doubs, Jura and Territoire de Belfort, the first three of which all contain important cave systems. The Franche-Comte is brimming with sites of outstanding natural beauty, including Alpine meadows, lakes, cirques, waterfalls, thick forest and some of the most beautiful rivers in France. Glaciation, high rainfall and copious Spring snowmelt has encouraged plentiful erosion on the predominant Jurassic limestone landscape, resulting in a full range of karst features, including of course, several thousand cave systems.
Where is it?……….
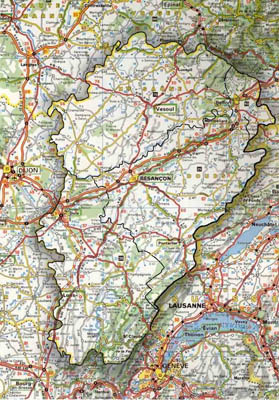
As you can probably appreciate from the map extract, the area is quite a large one. It nestles up against the Franco Swiss border immediately east of Dijon. We will be based roughly in the middle in a picturesque little town called Ornans which is located on the D67 about 20km south of Besancon. The area is probably best reached using the Dover – Calais or Folkstone – Calais crossings. A route is available which cuts south east around Reims and Dijon which negates the need to get tangled up with Paris. An alternative more elongated route swings up into Belgium and down across Luxembourg to drop back into France at Nancy. The auto routes are all free of toll on this route but it does take a little longer.
A little about the local geology…………….
The region can be divided into three major zones, the
Mountains, the Plateau Ridges and the Lowlands. The mountains are located
in the east and follow a NE-SW axis along the Swiss border. They are quite
small mountains for the area, the highest peak being Cret de la Neige,
at 1718m high. A few Alpine style shaft systems can be explored in this
zone. Parallel with the mountains lies an extensive series of Plateau
Ridges, which range in height from 900m to 400m, stepping down gradually
from East to West. These gently undulating agricultural regions, are home
to the majority of the caves (including most of the major systems), particularly
around the spectacular river gorges separating the ridges. The final region,
the lowlands, occupies the north of the region, but includes only a few
notable caves, formed in isolated ridges. The waters drain North-West
from the eastern mountains to the Saone valley. To get there they have
to cross the plateau ridges, for which there are only two possible options,
via Cluses (narrow gorges cutting through the ridges) or via caves, which
is why the majority of cave systems are found within the Plateau Ridges
region.
The whole region has been subject to quite severe folding and faulting,
and this has had a powerful effect on cave development. Underground drainage
is predominantly directed along the axis of the folds. Since the dip is
generally shallow, underground streams can travel very large distances
and the separation from sinks to resurgence can be considerable (the longest
positive trace is from Seignes de Passonfontaine to Source du Maine, a
distance of 28km over a vertical range of nearly 500m). However, the narrow
widths of the synclinal folds acts as a limit on overall catchment areas
and consequently many major systems consist of single streamways, albeit
of great length. The resurgences are often large and impressive, but almost
invariably flooded for a considerable distance. The feeders to these Collecteurs
are predominantly vertical, simple shaft systems, of not very great depth
(commonly between 100m and 300m). Most peter out in mud chokes and impenetrable
cracks, but a few utilise tectonic fractures to connect directly into
the Collecteurs. There are probably many more of these, hidden beneath
a blanket of alluvium. A third type of cave passage is found in ancient,
fossil remnants, located in the higher beds. Due to the relative youth
of the Jurassic formation, these are quite scarce, but typically feature
large, dry tunnels, often adorned with huge, muddy formations.
So what are the caves like?……………..
The caves of the Franche-Comte are generally simple in
plan, with a series of vertical Dales like pots feeding long, linear streamways.
This is partly due to the geology and partly due to the relative youth
of the Jurassic formations. The caves are commonly wet, muddy and well-decorated,
often with large formations. Jurassic limestone can be thinly-bedded and
brittle, so care should be taken when climbing or traversing. The weather
is generally sunny, but punctuated by sudden and severe thunderstorms.
This can create real problems, for the water tends to flash through the
caves very quickly. Pitch heads should be rigged as far out of potential
flood water as possible and long trips into streamways are best timed
to avoid the late afternoons. The vast majority of caves in the Franche-Comte
are prone to flooding of one degree or another, so it is best to take
some food and survival kit on most trips. On the plus side, the water
is likely to drop as fast as it rises, so a few hours wait will normally
allow for a safe exit. Choice of personal kit can also be difficult. Many
of the dry caves can be very warm, requiring only the lightest of clothing.
On the other hand, the wet caves often require full wetsuits.
Over 5000 caves have been mapped, the majority of which are horizontal
systems. Approximately 100 caves exceed 1km, 50 exceed 2km, and no less
than 15 exceed 5km in length. No very deep caves exist, but of the vertical
systems, three exceed 300m in vertical range, and more than 50 exceed
100m. The region is equally famous for cave diving and includes some of
the most extensive submerged networks in Europe.
Click on the link to Caves for more information and surveys.
Click on the link to the Camp Site for booking infomation.
Gary Vaughan,
10th December 2018
Updated 20.01.20